Selecting the Best Oil Spill Booms
When an environmental incident occurs, reliable oil spill booms are your critical first line of defense, preventing widespread pollution and enabling efficient cleanup. The urgent need for rapid and effective spill containment cannot be overstated; it mitigates environmental damage, protects public safety, and helps avoid severe regulatory penalties and costly cleanups. Inadequate spill response poses immediate financial and reputational risks for any organization. This comprehensive guide is designed to help small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) and municipal organizations navigate the complex options and confidently select the ideal oil spill booms for your specific operational and environmental requirements, ensuring preparedness and compliance. This article will serve as your essential resource for understanding, comparing, and ultimately purchasing the right oil spill containment booms, detailing types, selection factors, deployment strategies, and compliance considerations, empowering you to make an informed investment in your spill preparedness plan.
What is an Oil Spill Boom and How Does it Work?
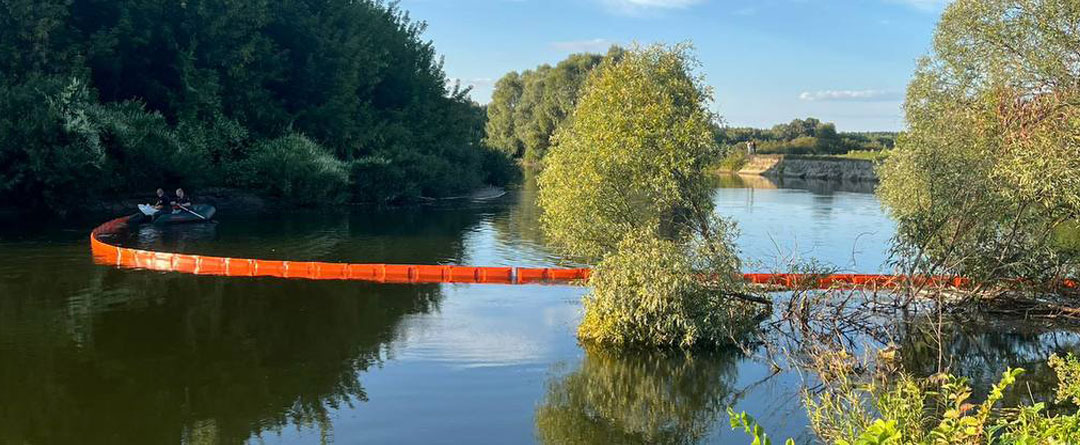
An oil spill boom is a temporary floating barrier specifically engineered to contain oil spills on water surfaces. Its basic function is to create a physical barrier that restricts the spread of oil, thereby concentrating it for easier collection and recovery. The core principle of boom containment involves deploying these barriers in strategic configurations, such as a ‘J-configuration’ or ‘U-configuration.’ These shapes are designed to funnel the spilled oil towards a designated collection point, preventing it from dispersing over a wider area. Main components of an oil boom include a freeboard, which is the part extending above the water to prevent oil from washing over; a skirt, which extends below the water to stop oil from flowing underneath; and ballast chains or weights, which keep the skirt upright and submerged.
The Critical Role of a Containment Boom in Spill Response
A boom for oil spill events is an indispensable tool, serving as the primary response mechanism for initial containment. It prevents the escalation of a spill, significantly minimizing its environmental impact. Effective boom oil spill deployment plays a vital role in environmental protection by safeguarding sensitive ecosystems, shorelines, and aquatic life from contamination. Beyond ecological benefits, containment boom use helps mitigate damages, reducing the overall costs associated with cleanup, limiting property damage, and preserving business continuity by controlling the spread of hazardous materials. Unlike absorbents that soak up oil, skimmers that remove it, or dispersants that break it down, a containment boom acts as a physical barrier, making it unique and essential for initial isolation.
Exploring the Diverse Types of Oil Spill Booms
Solid Flotation vs. Air Inflated Oil Spill Booms
When selecting oil spill booms, understanding the two primary construction types is crucial. Each offers distinct advantages based on the application.
- Solid Flotation Booms: These oil spill booms utilize internal closed-cell foam for buoyancy, making them inherently robust and highly puncture-resistant. Their construction ensures high durability, making them suitable for long-term or semi-permanent deployment. They are typically ‘ready-to-deploy’ with minimal setup.
- Offer high stability even in rougher waters, require minimal maintenance once deployed, and are very reliable.
- Can be bulky to store, leading to higher transport costs.
- Air Inflated Booms: These oil spill booms rely on air chambers for buoyancy, which usually requires an air pump for inflation prior to deployment. Their lightweight nature allows for compact storage and very rapid deployment in emergencies.
- Excellent for rapid response scenarios, highly portable, and efficient for storage.
- Susceptible to punctures, necessitate inflation equipment, and may offer less stability in very choppy conditions compared to solid flotation types.
When to Use Which: Solid flotation booms are often preferred for permanent installations around industrial facilities or as continuous barriers. Air-inflated oil spill booms are ideal for emergency response kits where quick deployment and portability are paramount.
Specialized Booms Oil for Specific Environments
Different environments demand specialized booms oil solutions to ensure effective containment.
- Calm Water Booms: Designed for protected areas like harbors, marinas, and enclosed ponds. These oil booms, often called fence booms, prioritize ease of deployment and are generally more cost-effective for stable conditions.
- Rough Sea Booms: These are heavy-duty boom oil systems built for open oceans or areas with strong currents. They feature larger freeboards, deeper skirts, and reinforced connectors to ensure stability and prevent oil escapement in challenging conditions.
- Icy Conditions/Arctic Booms: Specialized materials and designs are used for these boom oil types to resist freezing, maintain flexibility, and perform effectively in sub-zero temperatures, crucial for polar operations.
- Absorbent Booms: These booms oil not only contain spills but also absorb the oil. They are often filled with oleophilic (oil-attracting) materials and are suitable for smaller spills or as a secondary containment layer to recover residual oil.
- Fire-Resistant Booms: Constructed from high-temperature resistant materials, such as ceramic or stainless steel fibers, these boom oil models are used in situations where controlled burning of contained oil is necessary for rapid removal.
Permanent vs. Temporary Oil Booms: Applications and Benefits
Choosing between permanent and temporary oil booms depends on the duration and nature of the spill risk.
- Permanent Oil Booms:
- Use Cases: Ideal for high-risk, continually active areas such as refineries, ports, industrial facilities, or offshore platforms that require constant protection against potential spills.
- Benefits: Offer exceptional durability, are designed for prolonged exposure to harsh elements, and require minimal redeployment effort, ensuring continuous readiness.
- Temporary Oil Booms:
- Use Cases: Primarily for emergency response, short-term projects, or situations where oil booms are deployed as needed and then retrieved after use.
- Benefits: Characterized by portability, cost-effectiveness for infrequent use, and quick setup and takedown capabilities.
- Hybrid Solutions: Many comprehensive preparedness plans incorporate both permanent installations for consistent risk management and temporary response oil booms for immediate, flexible emergency deployment.
Key Factors for Selecting the Right Oil Spill Containment Boom
Material, Durability, and Environmental Suitability for Containment Booms
Selecting the appropriate oil spill containment boom material is paramount for its effectiveness and lifespan.
- Material Types:
- PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride): A cost-effective material offering good general resistance. It is common for inland and calm water containment booms.
- Urethane/Polyurethane: Provides higher tear and abrasion resistance, better chemical compatibility, and is more durable for varied conditions.
- Neoprene/Hypalon: Boasts excellent chemical resistance and extreme temperature tolerance, making it suitable for harsh marine environments.
- UV Resistance: Materials must be UV-stabilized to prevent degradation from sun exposure. This is crucial for ensuring a longer lifespan for oil spill booms that are stored or deployed outdoors.
- Chemical Compatibility: It is essential to ensure the boom material is resistant to the specific type of oil or chemicals it may encounter, such as crude oil, diesel, or various solvents.
- Abrasion Resistance: The boom’s ability to withstand rubbing against docks, rocks, or other vessels is vital, especially for long-term or dynamic deployments where wear and tear are expected.
- Environmental Suitability: The material choice must match the expected water conditions (calm, choppy, rough), anticipated temperatures, and the duration of exposure.
Size and Deployment Considerations for Oil Spill Containment Boom
The physical dimensions and deployment strategy of an oil spill containment boom are critical to its performance.
- Boom Height (Freeboard): Refers to how much of the oil spill containment boom extends above the waterline. This dimension is critical for preventing oil from washing over the boom due to wave action.
- Skirt Depth: The portion of the boom extending below the waterline is vital for preventing oil from escaping underneath, a phenomenon known as entrainment or sub-surface flow. Factors like current speed and oil viscosity influence the ideal skirt depth.
- Length Requirements: Determining the total linear feet of oil spill containment boom needed depends on the potential spill area, the perimeter of the facility, or the width of the waterway requiring protection.
- Current and Wave Action: These environmental factors directly dictate the required boom strength, stability, and connector integrity needed for an effective oil spill boom.
- Deployment Methods:
- Manual Deployment: Suitable for smaller, lighter oil spill containment boom sections, often deployed from shore or small boats.
- Automated/Mechanical Deployment: Involves the use of boom reels, trailers, or specialized vessels for rapid, large-scale deployment of heavy-duty booms.
- Anchoring Systems: The importance of appropriate anchoring, such as anchors, mooring buoys, or shore attachments, to maintain the boom’s position against currents and wind.
Storage, Maintenance, and Reusability
Proper care extends the life and ensures the readiness of oil spill containment boom assets.
- Storage Requirements: Practical aspects of storing oil spill containment boom include choosing between indoor or outdoor storage, considering climate control, and assessing compact versus bulky designs to preserve material integrity over time.
- Cleaning Procedures: Adhering to guidelines for cleaning oil residue from booms post-deployment is essential to ensure reusability and prevent secondary contamination during future operations.
- Inspection and Repair: Regular inspections for damage, such as tears, punctures, or connector wear, are paramount. Immediate repairs maintain operational readiness and prevent failure during an actual spill.
- Long-Term Value: Proper storage and maintenance directly influence the lifespan and readiness of oil spill booms, providing significant cost savings by extending their service life.
- Shelf Life: Consideration must be given to material degradation over time, even in storage, along with recommended replacement schedules to ensure peak performance.
Deployment, Compliance, and Sourcing Oil Spill Booms
Best Practices for Effective Boom Containment Deployment
Successful boom containment relies on meticulous planning and execution.
- Strategic Placement: Emphasize the importance of planning boom placement based on prevailing winds, currents, and water depth to maximize containment effectiveness. This prevents oil from moving beyond the boom’s perimeter.
- Configuration Techniques: Discuss common deployment patterns such as U-shape, J-shape, or exclusion booming, used to protect sensitive areas or funnel oil to a specific recovery point.
- Anchoring and Mooring: Detailed explanation of secure anchoring techniques and the correct use of mooring lines to prevent boom displacement from environmental forces.
- Rapid Response Kits: Highlight the importance of having pre-packaged oil spill booms and all necessary accessories readily available for quick deployment in emergencies, minimizing response time.
- Oil Recovery and Disposal: Briefly touch upon the subsequent steps after containment, including skimming collected oil and responsible disposal of contaminated booms and absorbent materials.
Regulatory Compliance and Industry Standards
Adhering to regulations is a non-negotiable aspect of managing oil spill booms.
- Understanding Requirements: Outline the necessity of understanding and adhering to local, national, and international regulations for spill prevention and response. These laws dictate how spills must be handled.
- Key Agencies: Mention relevant regulatory bodies, such as the EPA (U.S.), the Coast Guard (U.S.), or international maritime organizations (e.g., IMO), which set standards and enforce compliance.
- Industry Certifications: Explain the importance of oil spill booms that meet specific industry standards (e.g., ASTM, ISO) for performance, material quality, and environmental safety.
- Spill Response Plans (SPCC, FRP): Discuss how the selection and availability of oil spill containment boom are integral components of mandatory spill prevention, control, and countermeasure (SPCC) plans and facility response plans (FRP). For official spill containment guidance, consult the NOAA Office of Response and Restoration.
Finding Trusted Suppliers for Your Oil Spill Booms
Sourcing oil spill booms from a reliable supplier is crucial for preparedness.
- Key Supplier Attributes: What to look for in a reputable supplier, including extensive industry experience, a proven track record of product quality, and adherence to relevant standards and certifications.
- Product Range and Customization: Assess suppliers based on the diversity of their oil spill booms and their ability to provide tailored solutions for unique operational needs or environmental challenges.
- Customer Support and Training: The importance of responsive customer service, readily available technical support, and potential training programs for boom deployment and maintenance to ensure proper use.
- Certifications and Guarantees: Look for suppliers who provide verifiable product certifications, offer warranties, and clearly state performance specifications for their oil spill booms.
- Logistics and Availability: Consider a supplier’s capacity for rapid delivery, especially for emergency response oil spill containment boom purchases, and their consistent inventory levels to avoid delays.
Conclusion
Selecting the optimal oil spill booms is a critical investment in environmental protection, operational continuity, and regulatory compliance for any business or municipality. We’ve explored the main factors to consider: understanding different types, such as robust solid flotation versus portable air-inflated booms, and specialized booms for unique environments. Evaluating key selection criteria, including material durability, appropriate size, and effective deployment strategies, is essential. Addressing practical considerations like proper storage and routine maintenance will ensure your equipment is always ready. Don’t wait for a spill to occur. Be proactive in your preparedness by carefully assessing your specific environmental risks and operational needs. Utilize this comprehensive guide to compare oil spill booms options, and connect with reputable suppliers to ensure you invest in the most effective oil spill containment boom solutions for your preparedness plan. Explore our recommended oil spill containment boom products and consultation services today to secure your facilities and protect our environment.